Your cart is currently empty!

Gaziantep Landfill Gas
Project Description
This project supports collection of landfill gas and generation of 5.655MW of electricity at a landfill serving Gaziantep City, Turkey. The project is expected to reduce more than 91,000 tonnes of CO2e emissions each year. Credits are generated from two pieces of the project: (1) avoiding the emissions of methane (a potent greenhouse gas) into the atmosphere and (2) using the power generated from the methane (natural gas) to displace dirtier fossil-fuel-produced power coming from the electric grid. The project clearly required carbon revenues to achieve these two goals and therefore generates high-quality carbon offsets.
Key Information
Due Diligence
CNaught maintains a very high quality standard for all projects in the portfolios we manage. To ensure that a project meets this standard, we perform due diligence that’s backed up by third-party ratings agencies’ independent due diligence.
Additionality: This project has high additionality, meaning it is very unlikely that this project activity could have occurred in the absence of carbon funding. Landfill gas capture programs were very rare in Turkey when this project began (only 9 out of 2800 landfills captured methane!1), suggesting that the activity is not common practice. In addition, the project thoroughly demonstrated both regulatory, and most critically, financial additionality through a rigorous investment barrier analysis. Calyx Global has highly rated this project specifically due to its robust investment barrier analysis.Over-Crediting: This project has a low risk of over-crediting due to the fact that its emissions reductions are a direct measurement of the methane captured and combusted or used for energy. However, Calyx Global did cite that the project used a default value of 10% natural oxidation in their baseline calculation, which could result in slightly increased emissions reductions calculations. Natural oxidation is the process in which methane can sometimes permeate the cover sealing the landfill and migrate upwards, where it is oxidized and converted into CO2. If projects use an oxidation factor that is too low, they risk over-calculating the amount of methane they capture. During our due diligence process, we reviewed the Gaziantep landfill’s geology, location, and size and found that it is unlikely to have a <20% oxidation rate, so the use of this default value could lead to slight over-crediting. However, the project uses a very conservative estimate of the global warming potential of methane, which leads to under-crediting that would more than counteract any issues that their oxidation rate presents.Durability: This project activity is highly durable as its emissions reductions are considered permanent, since its methane reductions cannot be reversed. There is also no risk that the project activity would lead to the creation of new landfills and thus additional methane emissions.Double-Counting:The project credits have a very low risk of being double counted. There are no regulatory obligations being met by the project activity and the project’s registry, Gold Standard, has mechanisms in place to ensure that the project is not registered in any other programs.
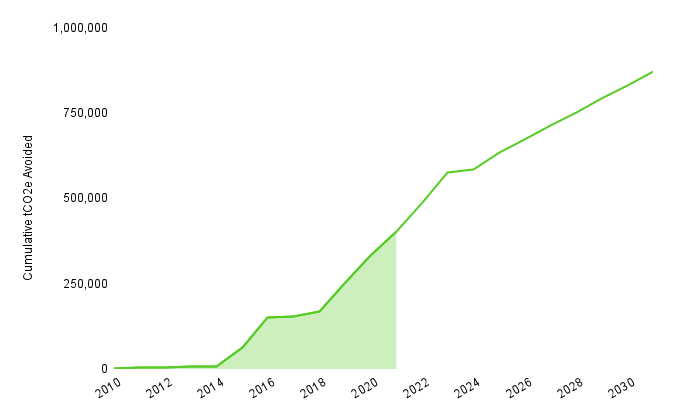
As the project continues to operate, its climate impact is continuing to grow! Figure shows the cumulative carbon dioxide emissions that this project has avoided so far, shaded in green. Note: Unshaded area represents the emissions reductions the project estimates it will avoid. Projects don’t issue credits based on these estimates, credits are issued once they receive verification of their avoided emissions. Verification can take a long time to do, so there is often a lag between the current year and the most recent year that they issued credits. All data post 2024 is interpolated.
Beyond Carbon
Community and biodiversity co-benefits
This project provides significant community, health, and sustainable technology benefits.
Community: This project has trained and hired local residents to help operate its facilities, supporting the local economy. It also hosts training sessions for operators of other landfills enabling the project activity to be performed at landfills elsewhere in Turkey. Human & Environmental Health: This project prevents contamination of local water supply and helps improve air quality. The project also prevents the risks of potential fires or explosions by capturing the methane produced by the landfill. Sustainable Technology: This project introduces an important sustainable technology to Turkey. Landfills are a significant source of methane emissions both in Turkey and throughout the world. Before the project began, Turkey had over 2,800 landfills and only 9 of those were collecting landfill gas1. This project, as well as other early landfill gas projects in Turkey, helped introduce this clean technology to Turkey, and has supported the scaling of implementation throughout the country in recent years.
Risk of Reversal
This project has no risk of reversal because its avoided emissions are not subject to being undone.
Registry & Verification
Third Party Labels
Project Location
Project data sourced from CNaught carbon marketplace. Information may be updated periodically.